7/03/2007
Giving Voice to Words
just the basic meaning of the words. Explore creative ways to use type
including student work, posters, and fanciful type treatments. Do
typographic exercises that allow you to expand your own creative use
of type and fonts. We, of course, will be using Photoshop to do this.
In class example: Glass Text
Easier:
Gel Text
Light Burst: Working with Channel Layers
Harder
Striped Text:
Student's choice:
Choose your own
6/26/2007
Layer Masks
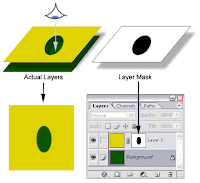 Layer Masks are a very powerful part of Photoshop and that is for a couple of reasons:
Layer Masks are a very powerful part of Photoshop and that is for a couple of reasons: - Layer Masks are editable selections that play an important role in non destructive editing
- Layer Masks offer flexibility because they can be almost completely treated as a full gray scale image, which allows the use of filters, selection tools, adjustment tools, etc.
- They have a visual strength, meaning that with a short look on the layers you can see how they affect the image
- They offer extra flexibility by being part of vector masks, layer sets, adjustment layers, etc.
- Layer masks allow you to save selections.
- Layer masks can be applied to any layer except the Background. *one must convert the background to a layer to use).
To understand layer masks you have to remember the following:
- The color black in a layer mask hides the corresponding pixels in the linked layer (actually makes those pixels transparent).
- The color white leaves the corresponding in the linked layer intact; it doesn't do anything with them
Fade layer
Adjustment Layer
Exposure Adjustments
6/25/2007
Quick Masks
1) Masks are non-destructive--none of the original work is edited or deleted. It is simply hidden.
2) Masks are flexible--they can be changed at anytime to reveal or hide areas.
Quick Mask:
Quick Mask function is actually a selection viewed in a different mode. Rather than the dotted-line marquee, it is represented in varying shades of red.
*Quick Masks are not permanent.
*The Color and opacity of the mask can be changed by clicking the Quick Mask icon.
Tutorials:
Bright Eyes (basic/start here)
Butterfly Partial Color
Using Masks to Remove the Background
Learn Hawk-Layer Masks
Try the image in the tutorial, then do one on your own!
5/22/2007
PDF stands for PORTABLE DOCUMENT FORMAT. A universal file format that preserves all fonts, graphics, and colors of a source file, regardless of the platform or application used to create it. These files are created using Adobe Acrobat Professional. These files can be shared, viewed and printed with individuals having Adobe Acrobat Reader, a free application, installed on his or her computer.
PDFs are a good way to publish your work for the following reasons.
- They are cross platform compatible. Documents look the same on a PC or Mac.
- They are secure--Users can view and copy segments however users can not edit or resave your work.
- They print the way you want them to. PDF files can produce sharper print outs than simply printing the browser screen.
How to Convert A Microsoft Word Doc to a PDF using Adobe 6.0
1. Open file that you wish to convert
2. From the menu bar, Select Adobe PDF (Optional can select from Tool Bar)
3. Select “Convert to Adobe PDF”
4. The Save As box will appear. *Note converted file is saved in the same directory as the source file using the same file name—adding pdf.*
5. The Adobe PDF Acrobat will automatically open the document for your review.
6. File>Document Properties, *Add Key words and ensure pdf title fits your file.
7. Select Save
8. Close
*The converted files also use the same printer settings and page orientations that you set up in the Office document.*
Converting pdf into other formats:
1. Open pdf in Adobe Acrobat
2. File>Save As
3. Select the format you wish
4. Click Save.
Design Tips on using PDF on Websites:
- You should use PDF only for documents that users need to download and print.
- Avoid using PDF files for on-screen reading. PDF text is optimized for printing not for reading on a browser.
- Create a gateway HTML page that summarizes the PDF file in sufficient detail, including page count and file size. This will let users decide whether it is worth downloading.
-
Ensure that your PDF document format is at least one version behind the latest offering. As with any Internet software, many users are slow to upgrade.
4/18/2007
Portfolio Project
A portfolio is a visual representation of your abilities, skills, capabilities and knowledge—it represents your potential. A Career or Personal Portfolio is an organized collection of evidence that shows your accomplishments both in and outside of school. A portfolio benefits by focusing on and revealing your achievements and accomplishments, as well as a variety of your learning experiences. It also gives you a greater awareness of where you need growth and experience.
The portfolio provides evidence of your potential by demonstrating what you have accomplished in the past.
***Portfolio is not the same as a resume. A portfolio can contain a resume.***
How?
You will use Photoshop, Fireworks, Dreamweaver and Flash as well as a combination of your HTML skills and other coding languages. These sites will be launched as well as burned onto cd.
Deadlines: Final site is due June 10, 2007.
Other Resources:Resumes Guides
Portfolio Samples (ideas)
Mission High School, San Francisco, SF
4/08/2007
Anchors Away: Using Name Anchors
A named anchor marks the place in the page to which a link jumps. A named anchor is simply an HTML anchor tagged pair (<>.....< / a>) that includes a name attribute. The named anchor serves as a target for links, allowing links to the middle of a page or wherever the named anchor is located within the document.
Resources: (How to Use a Name Anchor)
This is the easiest way to learn to use name anchors via this video tutorial. Please note it does require Quicktime:
Photoshop Support Video
Down and Dirty Notes:
To add an anchor tag to your page:
- Place your cursor at the point where you want to add an anchor.
- Click the yellow anchor icon or select Insert > Named Anchor from the Dreamweaver menu. (On the "Common" toolbar, click the named anchor icon--it looks like an anchor).
- Give the anchor a name (do not use spaces in the name).
- Click OK to add the anchor to the page.
- Note: You'll see a yellow, anchor icon where your cursor was (you can drag it to a different place in your document, later, if you like).
- Highlight the text or select the image you want to use as the link.
- In the Properties panel, locate the text box next to the word Link and do one of the following:
- Type the pound sign (#) followed by the name of the anchor (ie "#about us")
- Using the target icon to the right of the Link text box, click-hold and drag to the anchor icon on the page. Once the anchor is highlighted, let go. This will populate the Link text box with the pound sign followed by the anchor name.
3/26/2007
Optimizing Photos for Web

Optimization is the process of fine- tuning the display quality and file size of an image for use on the Web or other online media.
**Do NOT use Dreamweaver to resize your images--Please use only Photoshop**
RESOLUTION:
When you create a graphic for the Web, you must think in pixels, not in inches, millimeters etc. The resolution measurement used with the graphics and photos for print (pixels/inch) is useless on the web. The web browser measures the width and the height of a graphic in pixels, no matter if the graphic is 72 pixels/inch or 300 pixels/inch (ppi - pixels per inch). So, a 200x300 graphic looks the same size on the monitor with either 72ppi or 300ppi.
COLOR:
Only RGB! Browsers don’t understand other color modes such as CMYK, Lab and Multichannel,Saving JPG files with the Save as.. command
SAVE AS ...
In the Image Options section you specify the quality and the size of the saved file. The higher the quality, the higher th
e file size.
In the Format Options sect
ion you can chose from three JPG encoding options:
- Baseline (Standard) - You will leave this option selected almost always as this type of encoding is supported by
all browsers, even the oldest versions. Choosing this option you make your file "user friendly"
as there will not be people which cannot see your graphic.
- Baseline Optimized - This is a newer compressing algorithm that produces slightly better image quality, but it's not fully compatible with some old browsers.
- Progressive - This option produces a photo, that will display gradually (in a series of scans) when it is downloaded to the browser. With the first scan, a low quality image will be displayed, then, with the second scan will appear a better quality graphic and with the final scan will appear the high quality final graphic. You can specify the number of scans from 3 to 5. The Progressive mode produces larger files and is not supported by all browsers.
Once you are ready with the image corrections and you have the image with the proper pixel dimensions, then:
Go to File > Save For Web...
The "Save for Web" command is an easy and comfortable way to save graphics for the Web. It allows you to save files for the web in GIF, JPEG and PNG formats directly from a Photoshop file, and most important, without affecting the original. You can also resize the photo (the graphic).
Another good thing with the "Save for web" is that you can work with slices, saving each slice with different settings. T he slices can be saved with or without the HTML code.
he slices can be saved with or without the HTML code.
In "Save for Web" window you can see both the original of the graphic and the optimization preview side-by-side. This will help you to optimize the graphic making it to look very close to the original, retaining a small file size.
As we mentioned above, you can easy work with slices here. Just pick-up the slice selection tool, select a slice and assign it the desired saving options.
On the bottom of the window you will see file size and the average download time.
All other options are the same as with the "Save As.." command.
Step by Step guide to using Save As.
(from:http://www.e-cobo.com/design_tips/grdesign/optimizing_graphics_for_web.php)

